Q) In the given figure, AC is the diameter of the circle with centre O.
CD is parallel to BE. 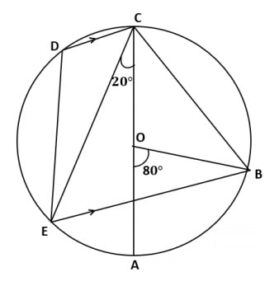
∠AOB = 80⁰ and ∠ACE = 20⁰.
Calculate:
(a) ∠ BEC
(b) ∠ BCD
(c) ∠ CED
ICSE Specimen Question Paper (SQP) 2026
Ans:
Step 1: AC is the straight line and hence ∠ AOB + ∠ BOC = 180°
∴ ∠ BOC = 180° – ∠ AOB
∠ AOB = 80° (given)
∴ ∠ BOC = 180° – 80° = 100°
Step 2: Let’s look at chord BC in the given figure:
Chord BC is making ∠ BOC at the centre and ∠ BEC at the circumference.
By angle at the centre theorem, we know that the angle subtended by a chord at the centre is twice the angle subtended on the circumference.
∴ ∠ BOC = 2 ∠ BEC
∴ ∠ BEC = ∠ BOC / 2
∴ ∠ BEC = 100° / 2 = 50°. (∠BOC = 100° calculated above)
Therefore, the value of ∠ BEC is 50°.
(b) Value of ∠BCD:
Step 3: Let’s connect chord AB and check the following: 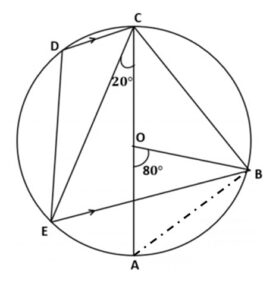
Chord AB is making ∠AOB at the centre and ∠ACB at the circumference.
By angle at the centre theorem, we know that the angle subtended by a chord at the centre is twice the angle subtended on the circumference.
∴ ∠AOB = 2 ∠ACB
∴ ∠ACB = ∠AOB / 2
∴ ∠ACB = 80°/ 2 = 40°. (∠AOB = 80° given in the figure)
Step 4: Next, we are given that CD is parallel to BE and when CE cuts these lines, alternate angles will be equal
hence, ∠ECD = ∠BEC
We just proved above that ∠BEC = 50°
∴ ∠ECD = 50°
Step 5: Now, from the given figure,
∠BCD = ∠BCA + ∠ACE + ∠ECD
∴ ∠BCD = 40° + 20° + 50° = 110° (∠ACE = 20° given in the figure)
Therefore, the value of ∠BCD is 110°
(c) Value of ∠ CED:
Step 6: From the diagram, we can see that BCDE is a cyclic quadrilateral, whose all 4 vertices are lying on the circle’s circumference.
We know that the sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180°.
∴ ∠BCD + ∠BED = 180°
∴ ∠BED = 180° – ∠BCD
∴ ∠BED = 180° – 110° (∠BCD = 110° calculated above)
∴ ∠BED = 70°.
Step 7: From the given figure, we can see that
∠BED = ∠BEC + ∠CED
∴ ∠CED = ∠BED – ∠BEC
∴ ∠CED = 70° – 50° = 20°. (∠BEC = 50° calculated above)
Therefore, the value of ∠CED is 20°.
Please do press “Heart” button if you liked the solution.
