Q) If 𝛼, β are zeroes of quadratic polynomial f(x) = 6 x2 + 11 x – 10, find the value of ![]()
Ans: In the given polynomial equation, to find zeroes, we will start with f(x) = 0
Therefore, 6 x2 + 11 x – 10 = 0
Step 1: Given that the roots of the polynomial are α and β.
We know that sum of roots (α + β) = ![]()
![]() α + β =
α + β = ![]() …………(i)
…………(i)
Next, we know that the product of the roots (α x β) = ![]()
![]() α . β =
α . β = ![]() ………… (ii)
………… (ii)
Step 2: Next, we need to find the value of ![]()
Let’s solve this to simplify:
![]() =
= ![]() ………(iii)
………(iii)
We know that (a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2 a b
or we can say that a2 + b2 = (a + b)2 – 2 a b
Therefore, α2 + β2 = (α + β)2 – 2 α β
Transferring this value in equation (iii), we get:
![]() =
= ![]()
Step 3: Next, we transfer values of (α + β) and α β from equations (i) and (ii)
![]() =
= ![]()
= 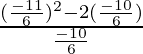 =
= 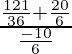
= 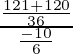 =
= ![]()
= ![]() = –
= – ![]()
Therefore, the value of ![]() is –
is – ![]()
Please do press “Heart” button if you liked the solution.
